SPECIAL CLINIC
FOR LASER
AND
PHOTODYNAMIC THERAPY
Other malignant neoplasia of skin and mucosal membranes
Other malignant lesions of skin and mucosal membranes.
Metastases are new colonies of tumor cells growing outside the primary tumor. Colonies that have less than 100 thousand – 1 million cells cannot be revealed by ultra-sound or CT diagnostics (micrometastases). When metastases reach the diameter of 2-5 mm, they become available for US and CT diagnostics. Establishment of metastases is associated with unfavorable prognosis. Such cancer is called a disseminated form. In order to stop growth of metastases radiation and chemotherapy are performed. Survival period is determined by the rate of metastatic growth and sensitivity of metastases to therapy. In average, 5-year survival is achieved in 1 of 5 patients who underwent surgery. Photodynamic therapy for metastases treatment is also performed though not as widely as in case of primary tumor. PDT is effective in solitary skin metastases. Some successful cases of effective PDT for breast cancer and melanoma metastases in lymph nodes and parenchymal organs were also reported. PDT is more effective than pleurodesis by cytostatics in treatment of metastases in pleura and malignant effusion.
Cancer of the tongue mucosa is an epithelial tumor with 80% squamous carcinoma. It occurs in 2-8 times more often in men than women. It is diagnosed more often in patients of 50-70 years old but may be observed at younger age as well. The tumor develops at the background of previous benign pathology (chronic inflammatory processes, pre-cancerous conditions). Risk factors: drinking alcohol, tobacco smoking, chewing tonic mixtures (nas, betel), occupational hazards (contacts with oil refining products, salts of heavy metals), poor teeth status (caries, odontolith, poorly made dentures), bad care of oral cavity, HPV. 70% of tumors are found on the lateral surface of the tongue. Pre-cancerous conditions include leukoplakia, papilloma, chronic ulcers. Patients often find them on their own but as a rule, pay no serious attention to that. The tumor at an early stage usually does not cause any disturbance, or feels only some roughness on the tongue. Therapy. The tumor at an early stage is removed by photodynamic therapy. The involvement of lymph nodes in the malignant process is associated with poor prognosis, because even complex treatment that includes distant gamma-therapy and extended surgery and chemotherapy cannot arrest the disease completely.
Cancer of the oral mucosa is an epithelial tumor with 80% squamous carcinoma. It occurs in 2-8 times more often in men than women. It is diagnosed more often in patients of 50-70 years old but may be observed at younger age as well. The tumor develops at the background of previous benign pathology (chronic inflammatory processes, pre-cancerous conditions). Risk factors: drinking alcohol, tobacco smoking, chewing tonic mixtures (nas, betel), occupational hazards (contacts with oil refining products, salts of heavy metals), poor teeth status (caries, odontolith, poorly made dentures), bad care of oral cavity, HPV. 70% of tumors are found on the lateral surface of the tongue. Pre-cancerous conditions include leukoplakia, papilloma, chronic ulcers. Patients often find them on their own but as a rule, pay no serious attention to that. The tumor at an early stage usually does not cause any disturbance, or feels only some roughness on the mucosa. Pain is usually associated with the advanced process when besides primary tumor there are metastases in lymph nodes. Therapy. The disease at an early stage is treated by removal of affected mucosal areas by laser coagulation or by photodynamic therapy. The involvement of lymph nodes in the malignant process is associated with poor prognosis, because even complex treatment that includes distant gamma-therapy and extended surgery and chemotherapy cannot arrest the disease completely.
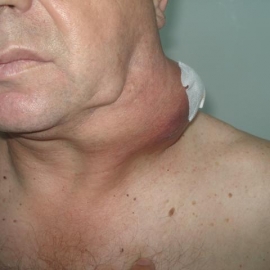
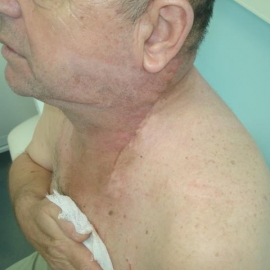
Treatment of skin cancer in the eye orbit and moreover in case of eyelid skin lesions is a complicated medical problem. Surgery and radiation therapy of eyelid skin lesions is limited because of possible serious anatomic functional disorders as far as loss of sight and is associated with early relapses and continued tumor growth. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) opens an opportunity for radical treatment with no reduction of eyesight but with high cosmetic effectiveness. Photodynamic therapy potential is clearly demonstrated in the photos of a clinical case. Patient K. first referred to the oncological hospital because of a lesion in medial angle of the eye of the rice grain size. It was diagnosed as basal cell skin cancer and surgical excision was performed. A year later a relapse developed in the site of post-surgical scar of a bigger size, which was exposed to radiation therapy, - close-focus radiotherapy. A new relapse developed again one year later, which involved both eyelids and the whole medial angle of the eye. The patient had consultations in cancer centers in Moscow and was offered an extended operation with the eye removal. In Krasnodar the patient had consultation by P.B.Popov, MD, PhD, who decided to perform photodynamic therapy in such complicated clinical situation.
Skin cancer of ear auricle is problematic site for surgery and radiation therapy of the face. Photodynamic therapy, a highly selective method, provides an opportunity to remove tumor radically with maximally preserved healthy tissues.